|
|
|
|
• EC • Season Cracking • Caustic Embrittlement • Intergranular • SSC • LME • MIC • SCC • HB-HE-HIC • Fatigue • Erosion• Stray Current • Index |
|
Different Types of
Corrosion
|
|
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) |
|
|
Recognition of Stress Corrosion Cracking |
|
|
What is stress corrosion cracking?
Stress-corrosion cracking (SCC) is a cracking process that requires
the simultaneous action of a corrodent and sustained
tensile stress. This
excludes corrosion-reduced sections
that fail by fast fracture. It also
excludes intercrystalline or transcrystalline corrosion, which can
disintegrate
an alloy without
|
|
|
Mechanisms of Stress
Corrosion Cracking |
|
|
What causes stress corrosion cracking? Stress corrosion cracking results from the conjoint action of three components: (1) a susceptible material; (2) a specific chemical species (environment) and (3) tensile stress. For example, copper and its alloys are susceptible to ammonia compounds, mild steels are susceptible to alkalis and stainless steels are susceptible to chlorides. There is no unified mechanism for stress corrosion cracking in the literature. Various models have been proposed which include the following:
|
|
|
Prevention of Stress
Corrosion Cracking |
|
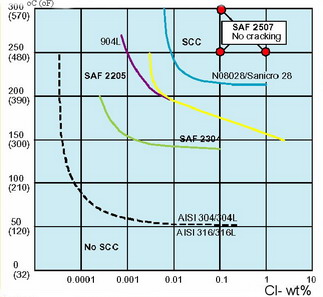 How to prevent
stress corrosion cracking? Stress corrosion cracking can be prevented through: How to prevent
stress corrosion cracking? Stress corrosion cracking can be prevented through:
|
|
|
For more details on Stress
Corrosion Cracking |
|
Where can I learn more about
stress corrosion cracking? More details on stress corrosion
cracking are included in the following
corrosion short courses which you can take as
in-house training courses,
course-on-demand, online
courses or distance
learning courses:
If you require corrosion expert witness or corrosion consulting service on stress corrosion cracking, our NACE certified Corrosion Specialist is able to help. Contact us for a quote. |
|
|
Home | Subject Index | Contact Us | PDF |
Copyright © 1995-2025.. All rights reserved. |
