|
|
|
|
• EC • Season Cracking • Caustic Cracking • Intergranular • Pitting • SSC • LME • MIC • SCC • HB-HE-HIC-HMx-HTHA • Fatigue • Erosion • Index |
|
Different Types of Corrosion
|
|
Hydrogen Blistering |
|
|
Recognition of Hydrogen Blistering |
|
|
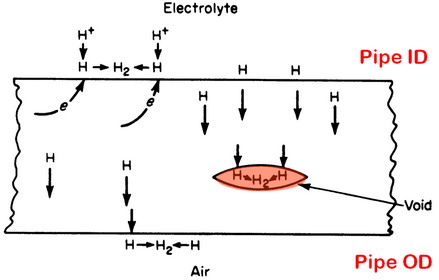
Hydrogen Blistering (HB) refers to the formation of subsurface planar cavities, called hydrogen blisters, in a metal resulting from excessive internal hydrogen pressure. Growth of near-surface blisters in low-strength metals usually results in surface bulges.
Mechanisms of Hydrogen Blistering What causes hydrogen blistering? Hydrogen ions are reduced to hydrogen atoms that adsorb on the steel surface. Some of the hydrogen atoms will diffuse through the steel and accumulate at hydrogen traps, typically voids around inclusions. |
|
|
When hydrogen atoms meet in a trap and combine, they form hydrogen gas (H2) molecules in the trap. The accumulation hydrogen gas inside the extremely small cavity will lead to the buildup of excessive internal hydrogen pressure. At certain times, this internal hydrogen pressure will become sufficient to cause the steel to blister.
Blisters occur usually in low strength steels (<80ksi yield strength) and are formed preferentially along elongated nonmetallic inclusions or laminations in linepipe steels.
|
|
|
Modeling, Prediction, and Prevention of Hydrogen Blistering |
|
|
How to select alloy steels for resistance to
Blistering?
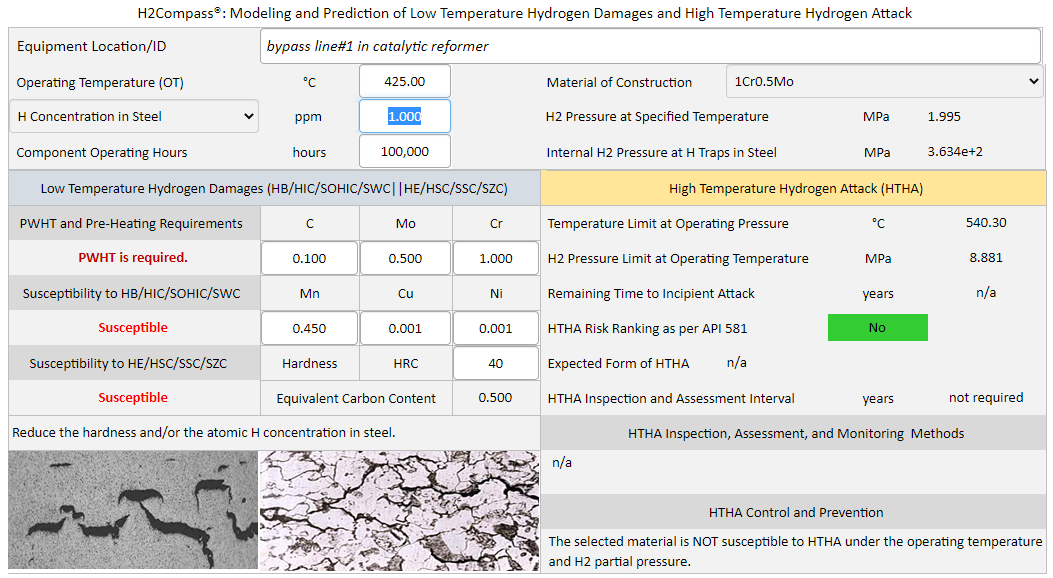
H2Compass is a powerful software for modeling and prediction of low temperature hydrogen damages and high temperature hydrogen attack (HTHA). H2Compass software provides instant answers to the above questions. The software can be used to determine the atomic hydrogen concentration in steels, the internal hydrogen gas pressure at hydrogen traps in steels, the steel's susceptibility to low temperature hydrogen damages, and the requirements for post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) and pre-heating.
Hto prevent hydrogen blistering? Hydrogen Blistering can be prevented through:
|
|
|
For more details on Hydrogen Blistering |
|
|
Where can I learn more about hydrogen blistering? More details on hydrogen blistering are included in the following corrosion courses which you can take as in-house training courses, course-on-demand, online courses or distance learning courses:
If you require corrosion expert witness or corrosion consulting service on hydrogen blistering, our NACE certified Corrosion Specialist is able to help. Contact us for a quote. |
|
|
Home | Subject Index | Contact Us | PDF |
Copyright © 1995-2024. All rights reserved. |