|
|
|||
|
• Consulting • Training • Expert Witness • Failure Analysis • Design Review • Corrosion Test • Inspection • Coatings • Materials • CP • >>> |
|||
|
|
|||
Corrosion Special Topical Papers |
|||
Protective Coatings: Performance Evaluation and Life Prediction*Dr. Jianhai Qiu
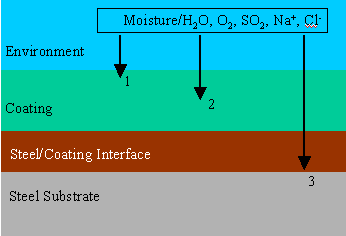
The Degradation Process of A Coating SystemA brief discussion on the degradation process of a coating system is helpful in understanding the nature of various methods for evaluation and life prediction. The durability of a coating system is ultimately determined by its capability to resist the ingress of moisture/water, oxygen and other ionic species such sodium and chloride (Fig.1).
In addition to this barrier function, metal coatings such zinc or aluminum on steel substrate (galvanized or aluminized steel) can provide sacrificial cathodic protection to the steel substrate. Anodic coating material such as zinc and aluminum applied on cathodic steel substrate represents a "safe" coating system in that at coating breaks, corrosion of the steel substrate would not be accelerated. In contrast, cathodic coating material such nickel and chromium platings applied on anodic steel substrate ensues the risk of accelerated attack on the steel substrate at coating breaks. There is a general consensus that the service life of zinc coatings is directly proportional to the coating thickness/zinc mass. However, no such generalization can be extended to polymer paints. The service life of a polymeric coating system can be roughly said to be proportional to the diffusion time (for example, the time it takes for a critical amount of moisture, sodium ion or chloride ion to reach the Steel/Coating interface). Once the reactants reach the Steel/Coating interface, corrosion of steel substrate can take place readily. Accumulation of voluminous corrosion product (rust) causes paint film to blister and this in turn accelerated the ingress of moisture/water and other species into the steel/coating interface. Performance evaluation methods can be based on the detection of the early changes in the dielectric property of a dry polymer paint film before any visible signs of staining or rusting occurs (stages 1 and 2 in Fig.1). The desirable attributes for the method of coating evaluation and life prediction is listed in Table 2. Table 2. Desirable Attributes for Methods of Coating Evaluation and
Life Prediction
|
|||
|
[Page 1] [Page 2] [Page 3] [Page 4] [Page 5] [Page 6] [Page 7] [Page 8] |
|||